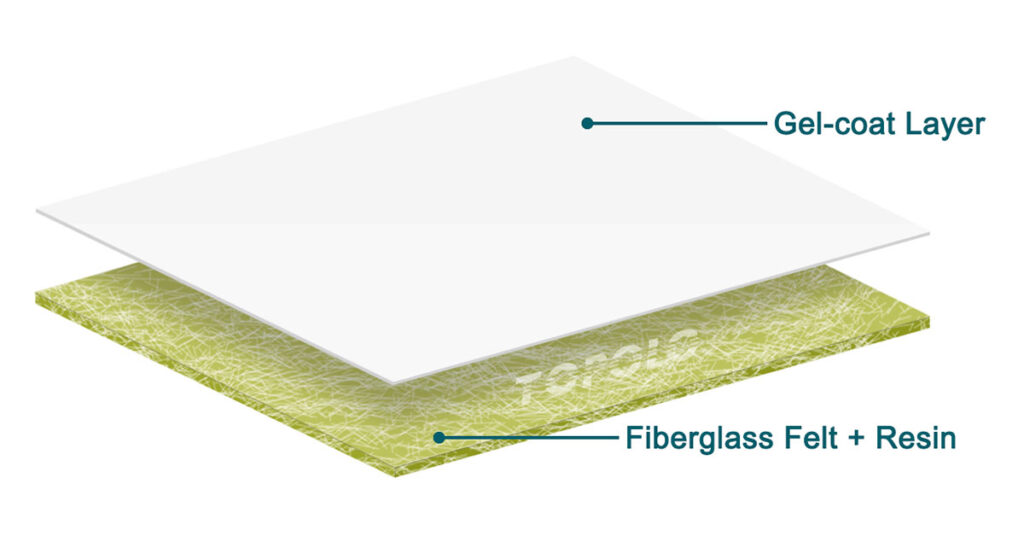
FRP Sheet Roll
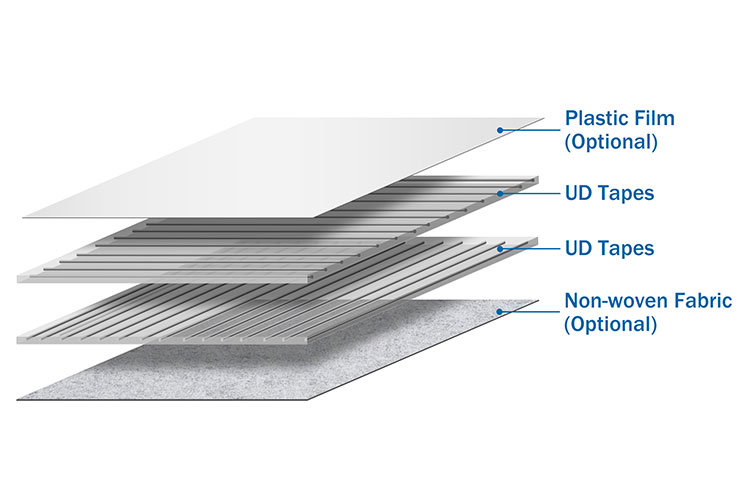
CFRT Sheet Roll
Although CFRT sheets and FRP sheets are both fiber-reinforced plastics and look similar in appearance and application, they have significant differences in material composition, fiber type and arrangement, mechanical properties, thermal properties, and production and processing procedures.
Material Composition Feature CFRT Sheets FRP Sheets Matrix Thermoplastic resin (e.g., PA, PEEK, PP, PEI) Thermosetting resin (e.g., polyester, epoxy, phenolic) Reinforcement Continuous fibers (carbon fiber, glass fiber, aramid, etc.) Short or continuous fibers (glass fiber most common) Fiber Arrangement Oriented continuous fibers → high strength & modulus Random short fibers or woven → strength uniformity varies
CFRT Shhet
Mechanical Properties Feature CFRT Sheets FRP Sheets Strength Very high (especially along fiber direction) High, depends on fiber type & arrangement Modulus High → ideal for heavy-load applications Medium → depends on fiber alignment Ductility Relatively low Thermoset FRP usually brittle, some can be toughened Impact Resistance Good, especially carbon fiber reinforced Depends on fiber & resin; glass fiber is moderate
Processing & Manufacturing Feature CFRT Sheets FRP Sheets Manufacturing Thermoplastic → thermoforming, welding, machining Requires mold curing, cutting or grinding; thermoset cannot be remelted Recyclability Thermoplastic → recyclable / re-moldable Thermoset → difficult to recycle, mostly mechanical grinding Production Speed Fast → suitable for high-volume production Slow → curing time depends on resin
Chemical & Thermal Resistance Feature CFRT Sheets FRP Sheets Chemical Resistance Good → thermoplastic resins are corrosion-resistant Moderate → depends on resin type Heat Resistance High-performance thermoplastics can withstand 200–300°C Depends on resin: epoxy ~150°C, phenolic higher UV Resistance Requires UV stabilizers Prone to aging → requires surface coating
Cost & Value Feature CFRT Sheets FRP Sheets Material Cost High → continuous fiber + thermoplastic resin Lower → glass fiber + thermoset resin Processing Cost Higher → thermoforming equipment required Lower → hand lay-up or spray molding equipment sufficient Cost-effectiveness High for high-performance applications More economical for large-scale, low-cost applications